Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): How Does it Actually Work?
Search is shifting. Today, I care less about Google rankings and more about whether AI tools like ChatGPT or Perplexity mention the brands I work with. This guide breaks down how generative engine optimization (GEO) works and how to show up in AI-driven answers.
Optimizing for AI mentions is the new SEO frontier.
After years of chasing Google rankings, I'm now equally focused on whether ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude mention products I promote.
Why does it matter?
Because more and more customers are switching to AI tools to answer their questions and research products.
If your content gets cited by AI, you gain credibility and visibility. If it doesn't, you're essentially invisible to a growing segment of searchers.
In this guide, I’ll break down how generative engine optimization (GEO) works, what drives AI citations, and how to apply it effectively.
What is generative engine optimization (GEO)?
GEO means structuring your content to be retrieved and cited by AI search engines like ChatGPT, Gemini, and others.
Since this field is still emerging, you might also come across terms like AEO (answer engine optimization), LLM SEO, or AI search optimization. They all point to the same underlying idea: making your content discoverable and quotable in AI-generated answers.
In reality, though, GEO is just another layer of SEO.
The difference is that search is no longer limited to Google’s SERPs.
Let’s unpack this.
What are generative search engines?
Generative search engines combine AI language models with web retrieval to answer user questions.
Unlike traditional search, they synthesize information into conversational responses, then cite sources they consider relevant and authoritative.
There are two main entry points to AI search:
Direct AI interaction platforms
Users start their search directly in an AI interface, asking questions conversationally via:
- Google AI Overviews or AI Mode
- ChatGPT (and the Search feature that connects it to the Internet)
- Perplexity
- Claude
- Microsoft Copilot
- Gemini
- Other AI chatbots
Traditional search with AI features
Users start on familiar search engines but receive AI-generated responses:
- Google AI overviews: AI-generated summaries that appear at the top of Google search results.
- Google AI mode: An experimental search interface that uses Gemini 2.0 to handle complex questions and allows follow-ups.
- Bing AI results: Microsoft's integration of AI-generated answers within their traditional SERPs.
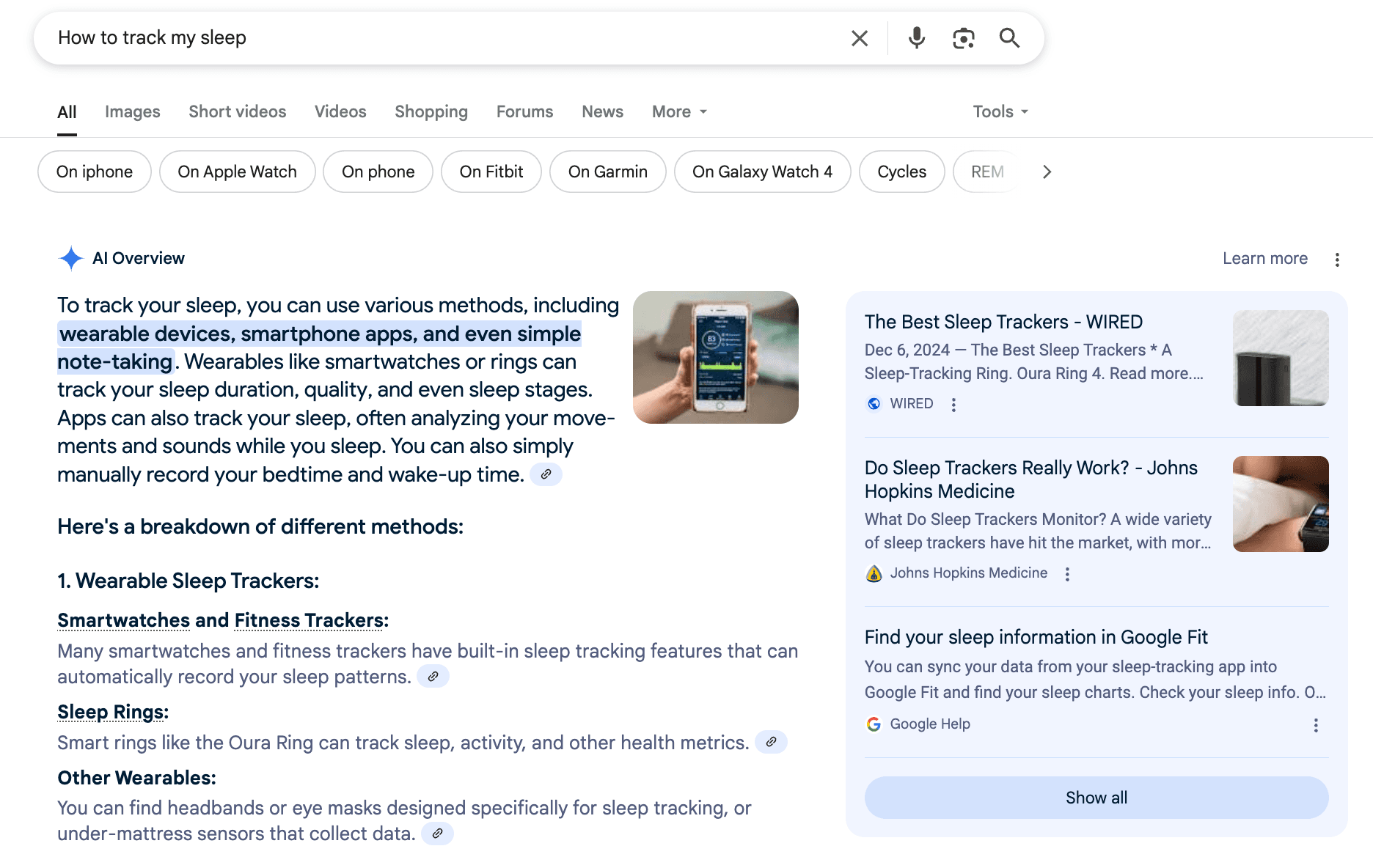
For example, you might type a long-form query like “What are the best sleep tracking solutions?” in ChatGPT and get a detailed breakdown of the options.

You can also find a similar answer through AI in Google search, along with helpful links and sources.
These AI overviews can occupy up to 75.7% of screen real estate on mobile and 67.1% on desktop.
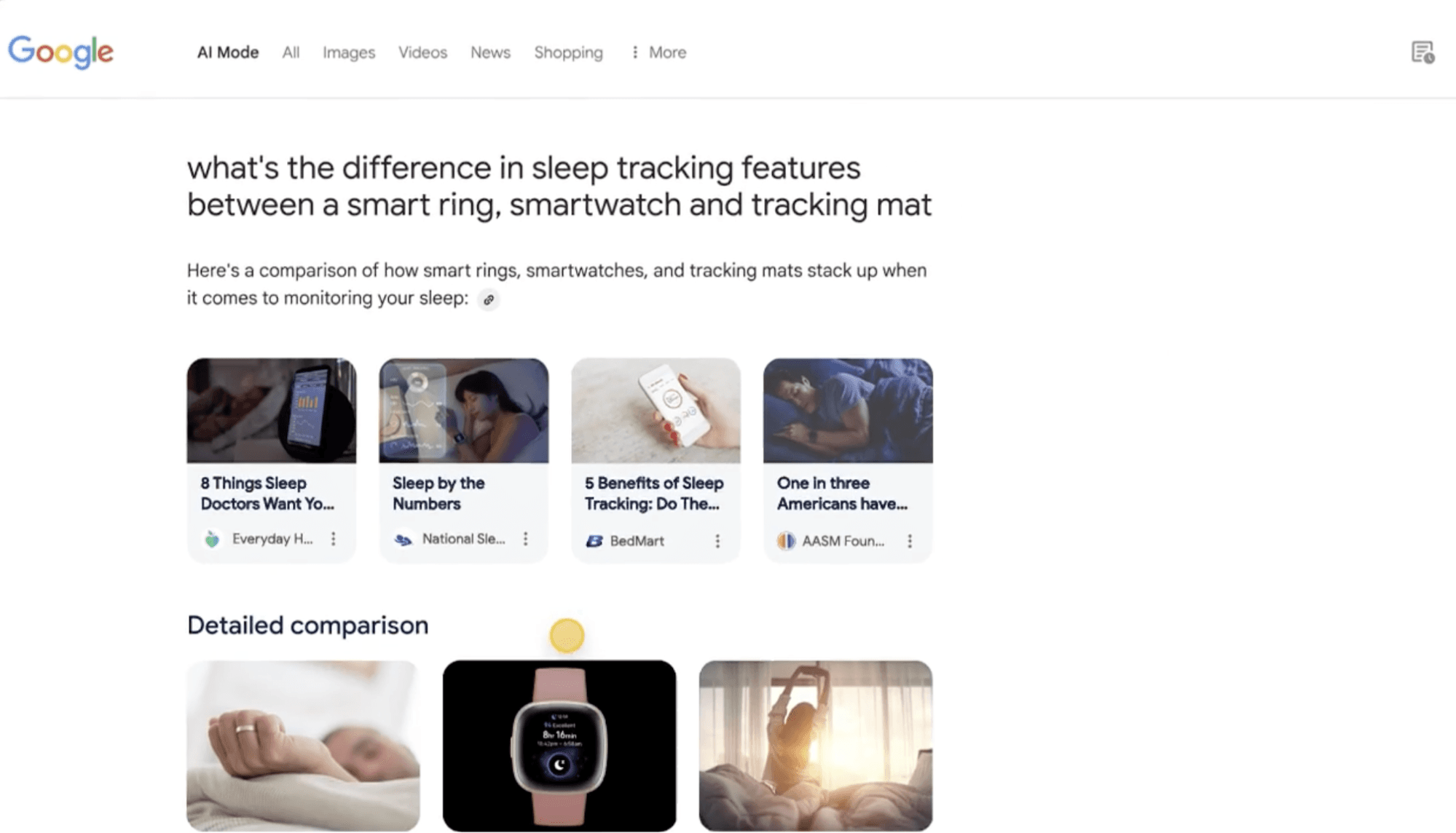
Finally, Google’s newly announced AI mode makes things even more interesting (especially for AI-anxious content specialists like myself).
It can tailor results based on your preferences, travel plans, life events, and even calendar data, creating a uniquely personalized search experience.
In other words, each user’s SERP might look unique.
How Do GEO Platforms Work?
Generative search engines (or simply AI search engines) analyze your question, gather information from multiple sources, and create a direct answer with citations.
Here’s a quick breakdown of this process:
- The AI analyzes what you're asking, including context from your previous questions. It identifies key concepts, intent, and any specific requirements in your query.
- It uses various sources to gather relevant information — depending on the model — like real-time web search and knowledge databases. For complex questions, it might run several searches on different aspects of your question simultaneously.
- The AI then evaluates the sources based on the relevance, authoritativeness of the source, information quality, recency, and more.
- Finally, it combines information from these sources into a coherent, conversational response.
Some platforms, like Perplexity and Google AI overviews, provide citations with direct links.
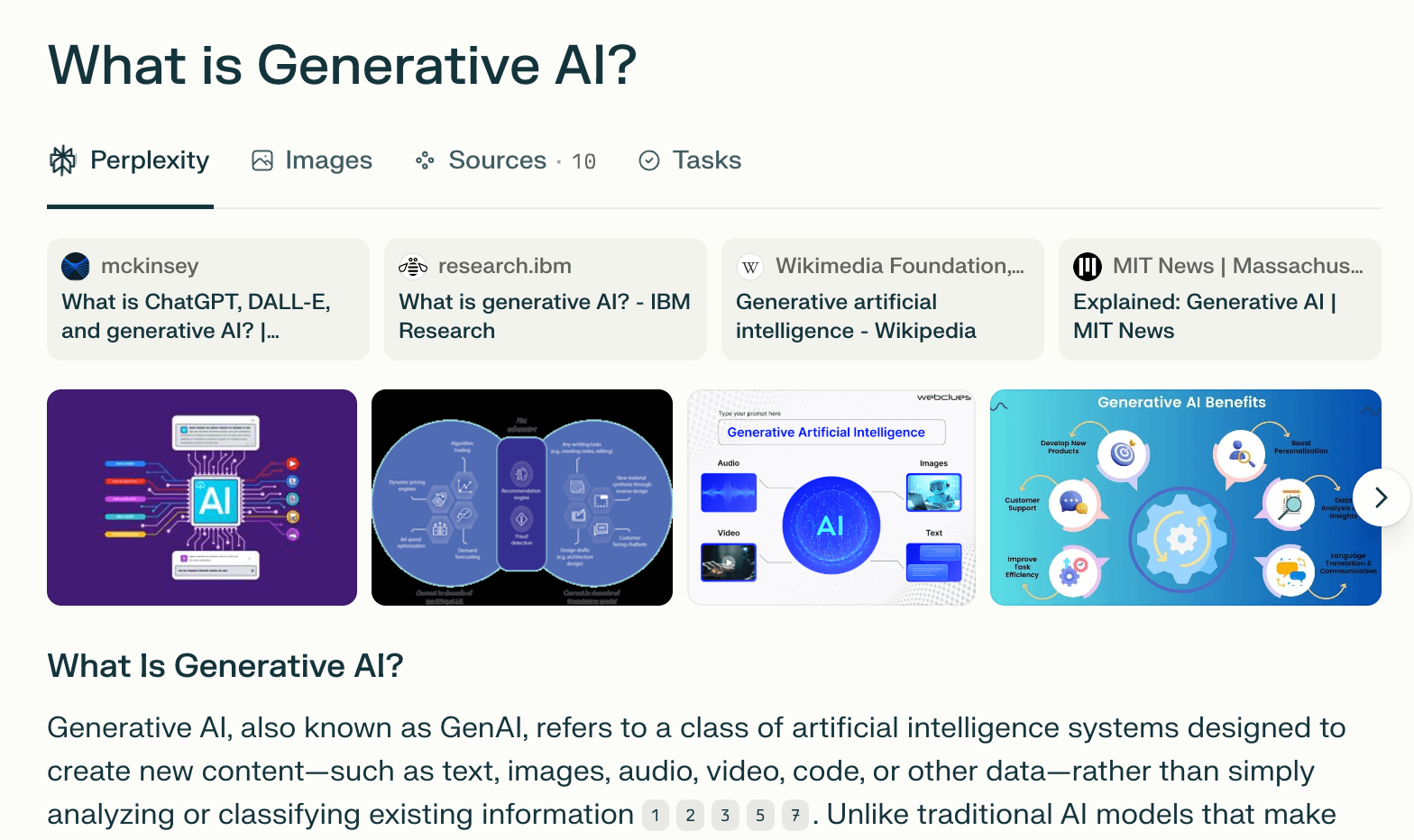
Others, like certain ChatGPT and Claude modes, might generate answers without visible attribution.
Meaning that your brand might get featured, but it won’t translate into clicks.

GEO vs SEO: Are they really different?
GEO and SEO share common ground, but they seem to operate on different principles.
Kevin Indig's analysis of over 7,000 AI citations reveals a surprising insight: the top 10% of most cited pages across AI platforms "have much less traffic, rank for fewer keywords, and get fewer total backlinks" than their SEO counterparts.
This suggests that strong traditional SEO metrics might not necessarily correlate with AI visibility.
And I’ve seen it firsthand.
For instance, I’ve seen ChatGPT feature my de-indexed article that wasn’t ranking for any relevant keywords:

That being said, I think that GEO and SEO still share certain similarities.
First, many LLM-based tools heavily rely on web content — think Perplexity and Gemini. Google’s AI features also pull content from search results.
A recent study analyzing AI tools that use live or indexed web content found a strong correlation between Google rankings and AI visibility. The higher a page ranks within the top 10, the more likely it is to be used in AI-generated answers.
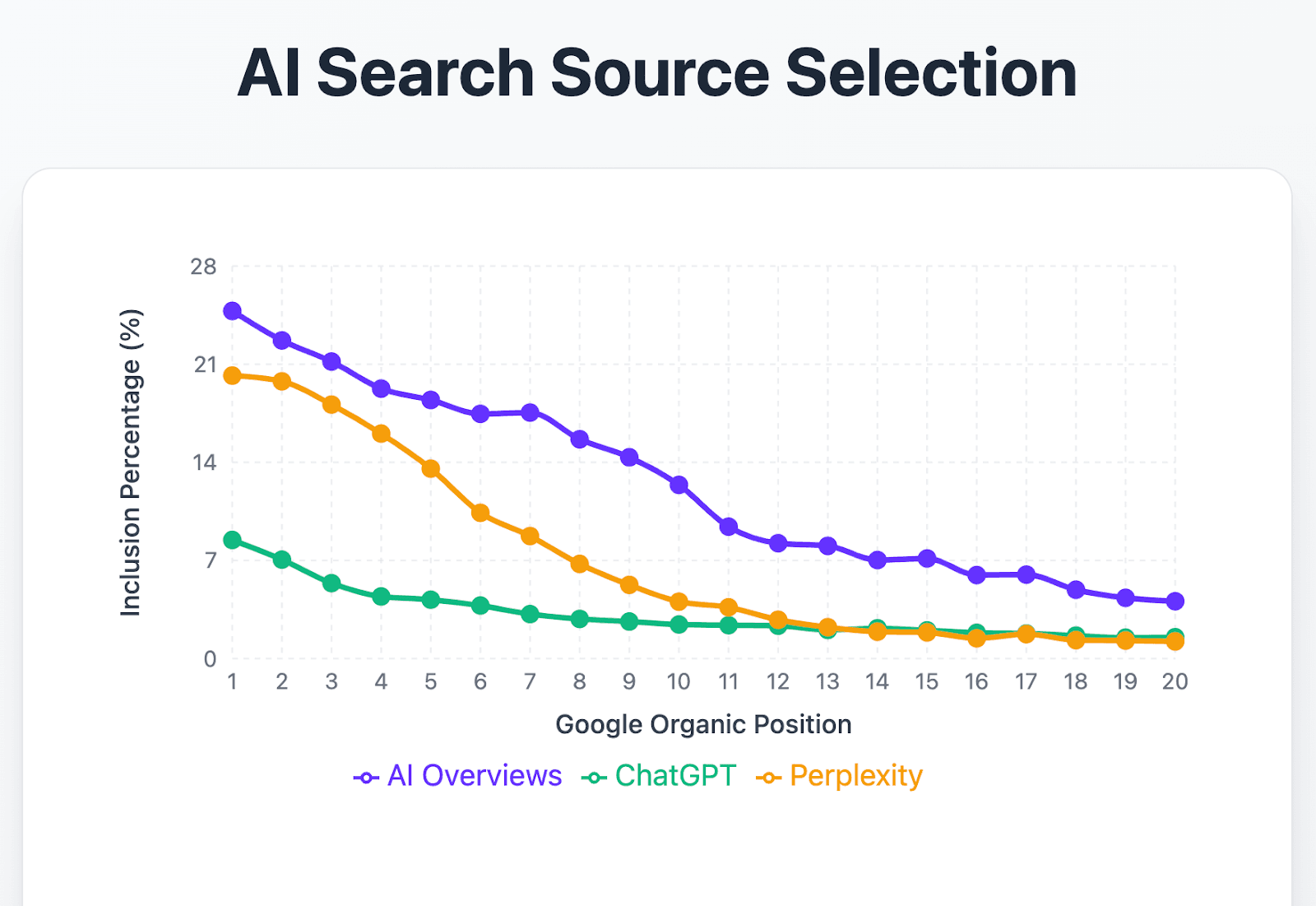
Second, many core SEO principles also stay true to GEO. Especially when it comes to:
- Having a strong, trustworthy brand
- Creating original, high-quality content
- Demonstrating external authority signals
We’ll explore this in detail later on.
How do users search in 2025?
To sum it all up, Search is becoming more complex and fragmented.
A recent study revealed that nearly 60% of Google searches now end without a click.

Meanwhile, AI search tools are gaining serious traction.
Another study found that 71.5% of US consumers have used ChatGPT and similar tools for searching, though only 14% use them daily.
In reality, most people use AI alongside Google and other platforms. For example:
- Quick facts? 79.8% still prefer traditional search.
- Complex questions? AI tools win.
- Shopping inspiration? Social search is taking over (e.g., 43% of Gen Z consumers start their online product searches on TikTok).
The takeaway?
Search visibility now extends far beyond direct search traffic.
But it’s not necessarily a bad thing.
When your brand gets mentioned in AI answers or appears in zero-click results, you're building recognition that sticks with users.
They might not click through immediately.
But consistent exposure across platforms creates cumulative awareness that influences decisions.
Do you need to work on GEO?
Yes, I’m totally convinced that GEO offers clear benefits. For example:
- Brand stickiness: When your brand appears in AI answers, it creates recognition that stays with users even without direct clicks.
- Appearing where users actually search: With more people using AI tools for searching, you need visibility across all discovery channels.
- Direct traffic gains: While a lot of search behavior in AI tools happens without clicks, many brands are seeing spikes in AI-driven traffic.
Lately, my LinkedIn feed has been full of founders and marketers claiming ChatGPT is driving meaningful traffic:
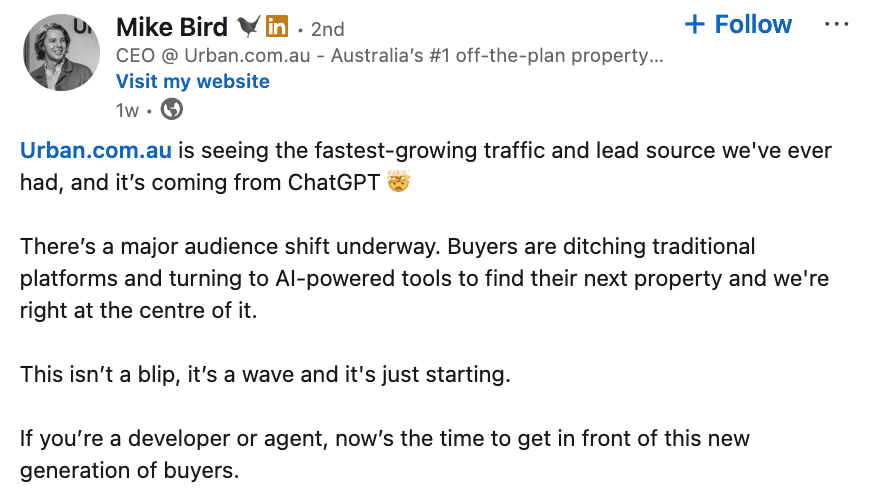
The caveat?
Don't obsess over optimizing for AI at the expense of content quality.
Focus on building genuine site authority rather than trying to game LLMs with technical tricks.
This helps you avoid the mistake many made with traditional SEO: prioritizing algorithms over audience value.
How to implement generative engine optimization (GEO)
The core principles of GEO mirror many long-standing content creation best practices.
“Classic SEO metrics don’t matter nearly as much for AI chatbot mentions and citations. The best thing you can do for content optimization is to aim for depth, comprehensiveness, and readability (how easy the text is to understand).” —Kevin Indig, Growth Advisor
“Classic SEO metrics don’t matter nearly as much for AI chatbot mentions and citations. The best thing you can do for content optimization is to aim for depth, comprehensiveness, and readability.”
In other words, it all comes down to what content marketers have been saying for over a decade: create content for people, not just search engines.
That said, GEO comes with its own unique twists and nuances.
Let’s go over the key steps you can take to succeed.
1. Focus on building brand awareness and authority
First things first: the stronger your brand is, the higher your chances of being featured, mentioned, and shared.
Recent research revealed a direct connection between brand awareness and AI visibility.
This study of 10,000 LLM queries found that brand search volume had a correlation coefficient of 0.18 with AI mentions, making it the second strongest correlation after domain rank (0.25).
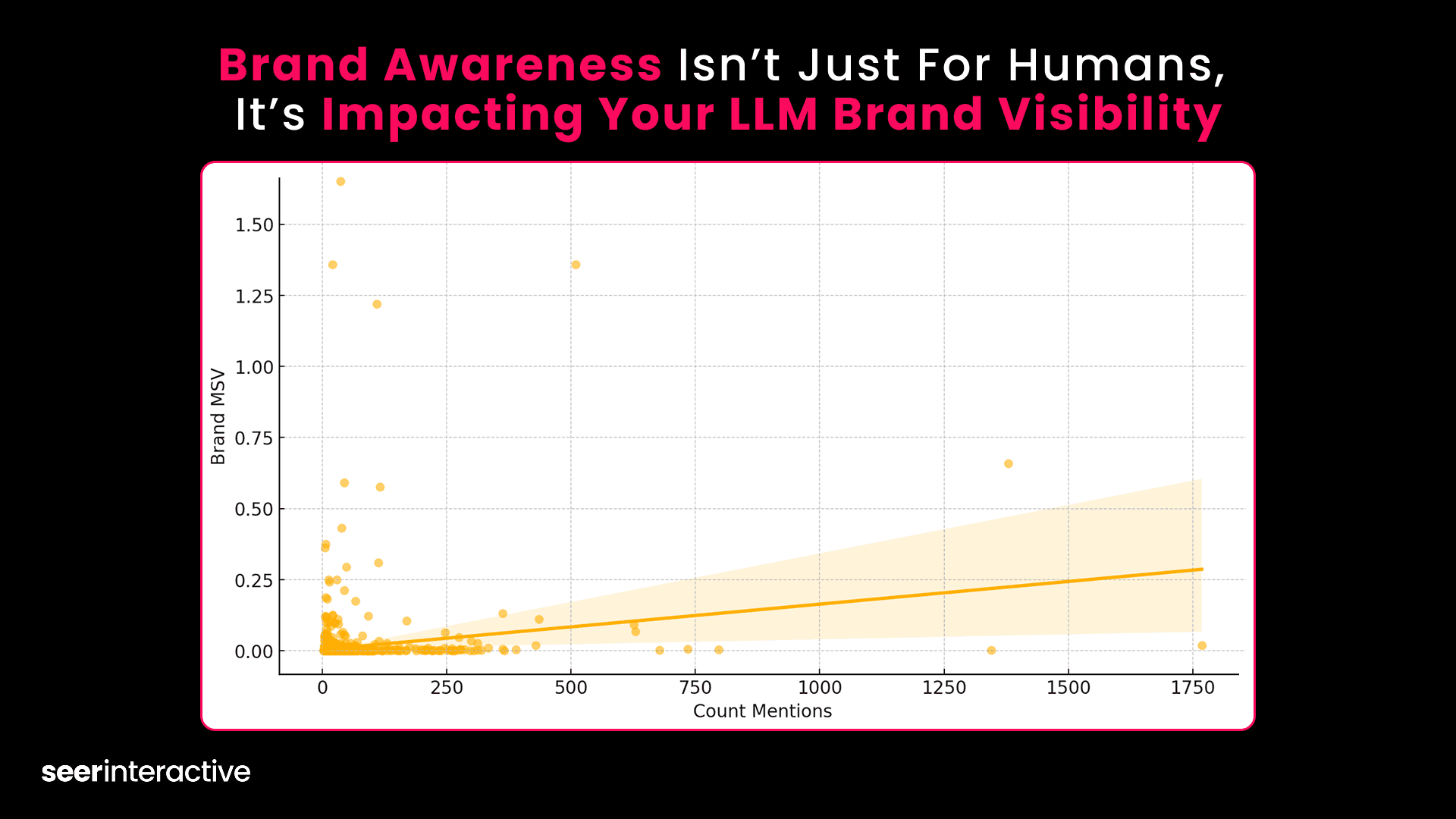
This connection is expected because established brands typically have:
- Stronger online presence: The more a brand appears on trusted sites, the more likely LLMs are to cite that brand.
- Higher domain authority: Well-known brands naturally earn more backlinks and authority signals.
- More publisher mentions: Recognized brands also get more coverage in credible news and industry publications.
It makes total sense to me.
For example, Semrush’s content and experts show up in nearly every important conversation about SEO and online visibility.
And it pays off.
Ask ChatGPT for the “best SEO tools,” and guess which brand comes up first?
Semrush, of course.

2. Share an original POV and publish research
One of the best ways to spark conversations around your brand?
Publish thought leadership content that makes people think, share, and reflect.
This helps you get external mentions, position yourself as an expert, and offer something AI content can’t replace — unique value and original opinions.
Here are some approaches you can use:
- Proprietary data: Run surveys with your customers, analyze product usage data, or compile industry benchmarks that only your brand can provide.
- Expert perspectives: Feature your internal subject matter experts sharing insights based on their unique experience and knowledge.
- In-house know-how: Share the lessons, best practices, and case studies that have come out of your own work: things you or your team members have tried, tested, and improved over time.
- Practical solutions: Create content that helps users take action rather than just absorb information, focusing on "How-to queries" that require more than just a shallow AI summary.
For example, SparkToro regularly publishes data-driven research and original point-of-view articles from its founder.
The result?
SparkToro comes up as the second result when you ask ChatGPT for the “best audience research tools.”
A visibility boost that reinforces SparkToro’s positioning as a go-to authority in audience intelligence.

3. Distribute your content and influence across multiple channels
AI systems don't just look at your website when deciding whether to cite your brand and how to describe it.
They analyze the entire digital ecosystem.
The same research confirms this: "The more a brand appears on trusted sites, the more likely LLMs are to cite that brand in answers."
Similarly, it states that "known brands are more likely to be picked up in credible news or industry coverage,” creating a virtuous cycle of visibility.
Here’s how you can implement this:
- Create platform-specific content: Develop native content tailored to each channel, like LinkedIn or Reddit, and repurpose it into various formats such as video, text, audio, and more.
- Secure speaking engagements and guest writing for your internal experts: Get your SMEs on industry podcasts, webinars, and conferences.
- Comment on trending industry topics: Actively participate in discussions on Reddit, Quora, and industry forums.
- Develop relationships with journalists: Become a reliable source for reporters covering your industry.
- Launch collaborative research projects: Partner with complementary brands to create annual industry studies or trend reports that get widely referenced.
For example, HubSpot usually publishes its annual State of Marketing report in collaboration with other brands.
In 2024, it co-produced the report with Litmus, Search Engine Journal, and Rock Content.
The brand and its partners then promote the report across multiple channels like social media.

From there, things started to pick up, and the report is shared by social media creators, publications, bloggers, and everyone in between.

The result?
HubSpot gets hundreds of organic mentions across different platforms, each one creating another chance for AI tools to come across and reference their expertise.

4. Create hyper-targeted content for nuanced search intent
Remember the traditional SEO search intent categories?
Informational for answering questions, transactional for buying things, and navigational/branded for finding specific businesses.
Things change dramatically when it comes to LLMs.
Semrush’s research showed that 70% of ChatGPT prompts consisted of unique queries rarely seen in standard search engines.
These are long-tail, highly specific, and complex questions that traditional SEO content often overlooks.
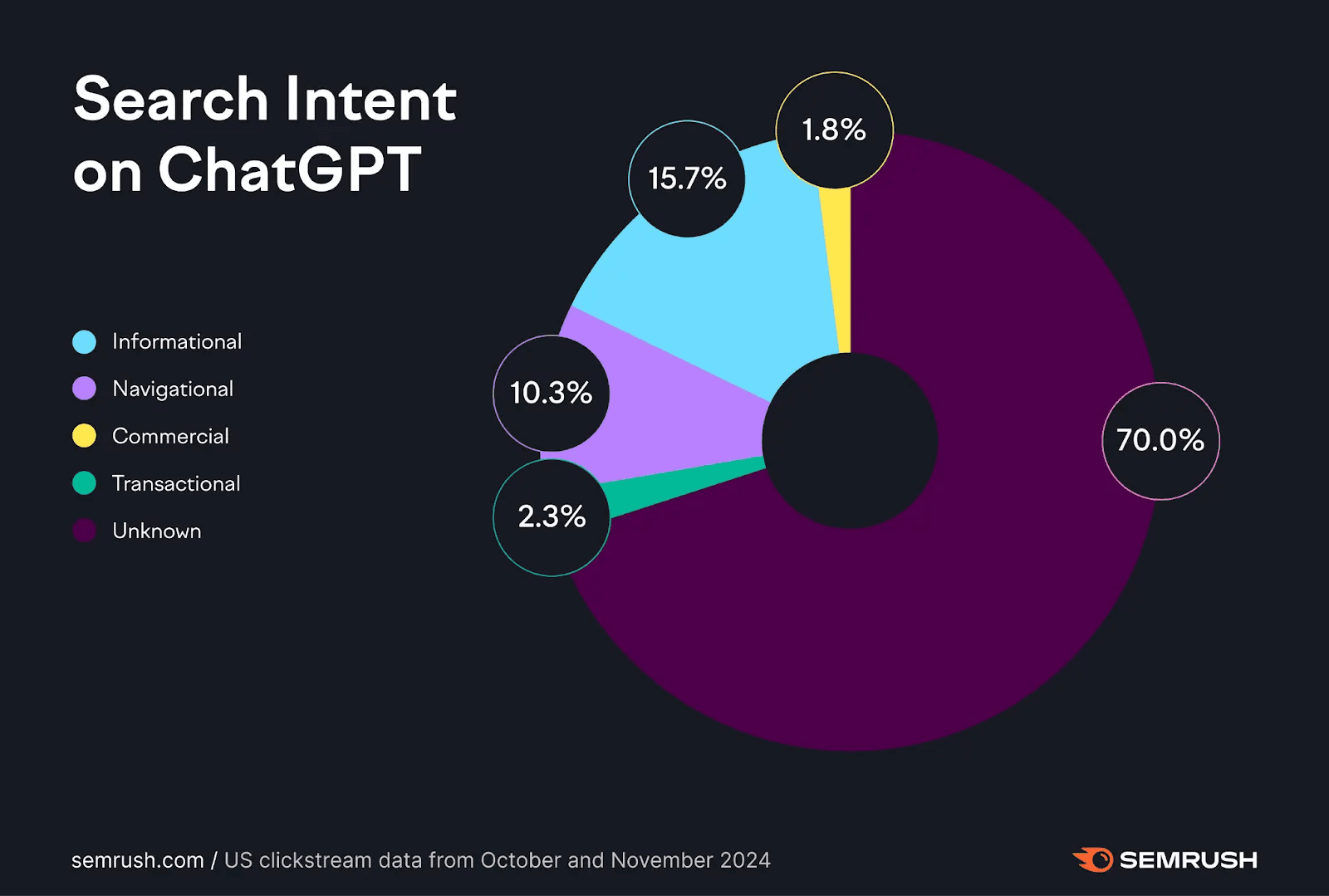
What does it mean?
AI-driven search prioritizes the most relevant piece of information, not the most broad coverage of the topic.
If a user searches for something like “how to write a welcome email for a fitness app,” they don’t want a 2,000-word guide on email marketing best practices.
They want a clear, specific piece of advice they can try out right away.
That’s why I really like the content Clay puts out.
They publish highly specific pieces on topics like “how to turn web visitors into leads with a warm outbound marketing play” and organically weave their product into the narrative.

5. Target mid- and bottom-of-the-funnel buyer intent
Let’s admit it: AI takes over the top of the funnel.
Generic "what is" content and high-level overviews? ChatGPT handles that now.
The middle and bottom of the funnel are where you can create real impact, and where AI tools are more likely to surface your content.
First, look for real-world customer insights: questions asked during demo calls, repeated sales objections, common pain points raised on social media, etc.
Next, structure your content around specific buyer intent. For example:
- Comparing options: When users are choosing between products or solutions.
- Looking for a replacement: When they’re unhappy with their current tool and looking for alternatives.
- Needing implementation: When they’ve decided to act and need help doing it.
Finally, create pages for each intent type and guide users toward action.
These could be comparison pages, help center guides, FAQs, feature pages, and case studies.
Once again, Clay does a great job with this.
Their blog is all about customer stories and product workflows that show how people are using the tool in real scenarios.

6. Structure your content to be surfaced by AI
How you organize your content also impacts whether AI tools will retrieve and cite it.
While structure has always mattered for SEO, AI tools place even greater emphasis on content that's easy to parse and extract information from.
Why?
Because LLMs analyze relationships between concepts, evaluate clarity, and tend to favor content that directly answers user queries.
To address this, structure your pages to have:
- Clear, question-based headings that mirror natural user queries
- Short, focused paragraphs with one idea per section
- Key information placed up front, with main points at the beginning of each section
- FAQ sections that create a natural question-and-answer format
- Bulleted lists and tables for easy information extraction
- Schema markup (structured data) to help AI and search engines better understand the context and meaning of your content
For instance, remember this de-indexed article of mine that got featured by ChatGPT?
I structured the entire piece to follow this approach:

This approach helped ChatGPT understand the page and cite it when I asked specific questions about building multichannel marketing strategies.
7. Take control of your brand narrative
With GEO, your brand identity is the sum of all your digital footprints
When AI describes your company, it pulls from whatever information it can find: your website, blog posts, press mentions, third-party reviews, and even social media comments.
That’s why it’s crucial to maintain consistent brand messaging in each of your content assets.
Here’s how:
- Use social listening to track brand mentions to spot and react to sentiment changes.
- Encourage customer advocacy through targeted review campaigns on G2, Trustpilot, and industry-specific sites.
- Create a brand messaging checklist and ensure all owned channels like your website, social profiles, and listings stay aligned with your up-to-date positioning.
- Monitor external platforms like Wikipedia and Reddit for outdated or inaccurate brand mentions and step in where possible by providing clarifications.
For example, Copy.ai has dramatically shifted its positioning several times over the past two years: from an AI writing tool to a GTM AI platform.
However, ChatGPT still features it as an AI writing platform, meaning its outdated positioning continues to shape how the brand is perceived.

8. Track your AI visibility over time
Monitoring how AI tools present your brand helps you catch important changes, track the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns, and even get a buy-in from stakeholders.
Of course, GEO doesn’t offer the same analytics as traditional SEO.
But there are methods you can try.
First, conduct a manual analysis.
Use this quick visibility test that Emilia Möller shared during our recent webinar at Semrush. All you need to do is ask various AI tools questions like:
- "What is [your brand]?" or "Tell me about [your brand]"
- "What are the best [product category] companies?"
- "How does [your brand] compare to [competitor]?"
- "Should I buy [your product]?" or "Is [your brand] worth it?"
- "What do users like/dislike about [your product]?"
Run those prompts and see how/whether your brand appears in responses. Note the tone, sentiment, and specific features mentioned.
You can also try a specialized AI visibility tool like the AI Toolkit we developed at Semrush.
It automatically checks how LLMs mention your brand and competitors and provides strategic insights.
This creates a feedback loop: implement changes, measure impact on AI visibility, then refine your approach based on results.
The GEO mindset: Being present where decisions happen
The shift to AI-led search represents the biggest change to content discovery since Google itself appeared.
However, GEO isn't a replacement for SEO.
It's an extension that acknowledges a fundamental truth: users now discover brands through multiple AI-mediated touchpoints before making decisions.
Who will thrive in this new environment?
The brands that build informational ecosystems that AI tools naturally recognize, reference, and recommend.
They create content worth citing, foster brand presence across multiple platforms, and build authority that resonates with the specific needs of their audiences.