How to Build a GEO Workflow That Makes Your Content LLM-Ready
Generative search is evolving faster than traditional SEO can keep up. This guide walks you through how to build a GEO workflow that helps large language models (LLMs) find, understand, and surface your content. You’ll learn what to prioritize, what to refine, and how to make AI visibility a repeatable part of your process.
Generative search behavior is already spiking. Capgemini Research Institute reports that 58% of consumers now use GenAI tools to search for products or services, up from 25% in 2023.
Tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity surface content based on patterns, formatting, and conceptual relationships, not just keywords or backlinks. That’s where generative engine optimization (GEO) comes in. GEO helps you create content that large language models (LLMs) can find, understand, and quote.
Tactics vary. Backlinko frames GEO as optimizing content for better visibility in LLM-generated results. iPullRank sees it as adapting SEO for changing search behavior.
Either way, the goal is the same: build content that earns visibility across AI-powered platforms. Making this process repeatable across every piece of content takes a workflow.
This guide is built for content marketers, editors, and strategists managing multi-asset workflows, especially if you’re creating thought leadership, educational hubs, or product-led content. No technical SEO background required.
You’ll get a step-by-step workflow to apply GEO across your content, from briefs and formatting to measurement. Plus, a free template to get started faster.
You can follow these steps manually, or run them inside Relato’s GEO Workflow — a built-in system that automates task assignment, brief creation, and review steps from start to finish.
1. Create briefs that support GEO from the start
GEO starts at the brief stage. If your team isn’t aligned on what question you’re answering and how you want to appear in LLMs, it’s easy to miss the mark.
Here’s what to include:
- Target query or prompt: Define the core phrase, question, or use case the piece is meant to answer.
- Working title and meta description: Help anchor the focus and reflect natural prompts.
- Concepts that need to be clearly defined: Highlight must-include definitions or terminology.
- Internal links to include: Identify related content to link from or link to.
- Competitor or source comparisons: Flag pages you want to improve upon or position against.
- Structural components: FAQs, how-to steps, checklists, or glossary entries — anything an LLM can easily extract and incorporate into answers.
- External sources or research to reference: Add any stats, studies, or industry examples that support your POV.
- Technical details: Note any schema, JSON-LD, or llms.txt updates that should accompany the page.
You can use a doc or spreadsheet to track these fields, but templates help standardize the process. In Relato, you can turn this into a reusable Brief Template that connects directly to the GEO Workflow, automatically assigning tasks and linking reviewers.
Try this: Download our free brief template to make this step easy, or use our Content Brief Assistant to set everything up for you.
2. Map your process from brief to publish
Once the brief is done, move straight into production. Adopt a defined workflow to avoid missing deadlines, delaying handoffs, or letting review cycles stretch longer than they should.
Use this sample sequence to structure your GEO process:
- Brief created
- Outline approved
- Draft written
- Editorial and SEO review
- Final copy approved
- CMS upload and formatting
- Publish
- Add to internal index
You can assign each step manually or automate the full workflow. In Relato, teams convert briefs into workflows in one click, with pre-assigned tasks and deadlines.
Tip: Build a reusable workflow in Relato that auto-assigns tasks, links back to the brief, and includes deadlines and review steps from day one. Learn how to automate it here.
3. Format your content to be LLM-friendly
Formatting shapes how your content is read and referenced. LLMs prioritize clarity and organization. Before you publish, make sure the draft is easy to parse and pull from.
To do that:
- Use short paragraphs and clear headers
- Separate key definitions, FAQs, and how-to steps
- Add lists or tables where appropriate
- Avoid cramming multiple ideas into a single section
- Keep one idea per section or block
Tip: Add a formatting check to your review stage so every piece gets a pass for clarity, headers, and extractable structures before publishing.
You’ll see this reflected in how tools like Perplexity highlight sources with clear FAQ sections or how ChatGPT summarizes answers that map closely to HowTo schema formats.
For more formatting tips and the why behind them, check out the explainer below.
How LLMs read your content
LLMs process language differently than humans. To format content effectively, it helps to understand how LLMs actually read, split, and prioritize your content behind the scenes.
Tokenization: breaking your words into pieces
LLMs break everything into tokens — small language units that might be a whole word, part of a word, or punctuation.
Example: The sentence “Email onboarding drives retention” is read as 5–6 tokens.
Why it matters: Long paragraphs and complex phrasing dilute clarity. Shorter sentences make your message easier to understand and quote.
Chunking: separating ideas into digestible blocks
LLMs read content in blocks, not pages. Each chunk has a token limit (often ~200–500 words). Too much in one block, and context breaks down.
Why it matters: If you want a specific answer or quote to surface in a response, keep it self-contained. Use structured headers and formatting like bullets or numbered steps to separate concepts cleanly.
Embedding: turning content into data
Once a chunk is processed, the model turns it into a vector — a numerical representation used to compare relevance across sources.
Why it matters: Consistent formatting, clear headings, and focused language make your content easier to embed accurately and more likely to be seen as reliable.
Understanding these mechanics helps you structure content that AI engines surface more often and more accurately.
4. Build in approvals and technical review
Review is where clarity, quality, and visibility often slip. Build it into your process early to prevent last-minute misses.
Editorial and SEO checks:
- Is the main question clearly answered?
- Are the explanations easy to quote out of context?
- Does the tone reflect your brand voice?
- Are internal links mapped to related topics?
- Does the formatting support chunking and scanning?
Technical checks:
- Metadata is complete and accurate
- Page added to sitemap or listed in your llms.txt (if your team uses one to guide crawlers or LLM indexes)
- Schema or structured data included (like FAQ or HowTo schema, if applicable)
- Tested in ChatGPT or Perplexity with a sample prompt
- All FAQs, glossaries, and lists are formatted cleanly
Relato lets you assign editorial and technical reviewers to specific steps so you can track approvals and comments in one place.
Tip: Assign both editorial and technical reviewers up front so nothing gets missed.
5. Link and log your content across your ecosystem
Search engines and LLMs are more likely to surface content when it’s connected and clearly organized by topic. After publishing, take a few minutes to link your new asset and record how it performs over time. Think of this as connecting your content’s ecosystem so both humans and LLMs can follow the trail.
Start by:
- Adding internal links from related posts
- Updating cornerstone or topic cluster pages
- Tagging the asset by prompt, topic, and review date
In Relato, you can organize and track all of this in one place. Custom fields and filters make it easy to see which assets cover similar prompts or topics, when they were last updated, and who owns each one.
Strong internal linking and consistent organization help reinforce your brand’s authority — both for your team and for LLMs learning to associate your content with credible, quotable sources.
Researchers and strategists are already tracking what’s known as “share of model” — an emerging metric that looks at how often a brand is cited or referenced across generative tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.
The more structured and interconnected your content is, the easier it becomes for models to recognize and reference your brand across different AI platforms.
Tip: Filter your content library in Relato by prompt keyword or topic tag to spot coverage gaps and avoid duplicate content before planning your next brief.
6. Measure what’s working and make improvements
Visibility in generative search isn’t static — it shifts with every model update, prompt variation, and trend. Measuring performance means combining manual testing with ongoing analysis.
Every quarter, test your core prompts in ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity to see where your content appears and how it’s represented. Record what you find directly in your Relato workspace — note any quotes, mentions, or patterns you want to revisit later.
As one Search Engine Journal contributor put it: “LLMs change their answers depending on the prompt, the session, and even the model update. So the real question isn’t ‘Am I ranking?’ It’s ‘When & how?’”
That’s why consistency matters more than single snapshots. Tag collaborators, leave comments, and update the workflow with new insights or follow-up tasks. Over time, these observations reveal which formats, topics, or structures consistently perform best in AI search.
Combine this qualitative data with metrics like impressions, click-through rate, and engagement in tools such as Google Search Console or GA4 for a complete performance view.
Tracking mentions and citations across AI platforms helps you understand your brand’s growing share of model — an emerging signal of visibility and authority in generative search.
Tip: Use Relato to centralize these notes and patterns inside each project workflow. You’ll have a clear record of when visibility shifts, what caused it, and which updates improved performance — no separate spreadsheets required.
Regular visibility testing and structured documentation keep your team responsive as AI search evolves — ensuring your content stays discoverable, quotable, and relevant.
Bring it all together
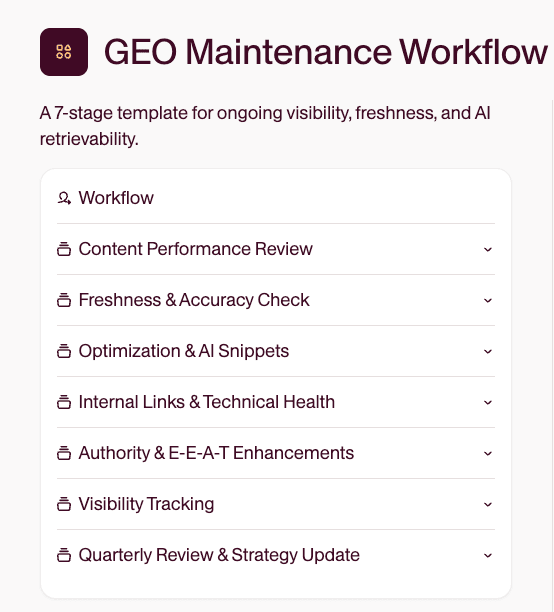
Now you’ve got a complete workflow for building and maintaining GEO-aligned content — from briefs and formatting to visibility testing and refresh cycles.
Ready to build GEO into your daily workflow? Get started in Relato to access the full GEO Workflow — complete with built-in briefs, automated task tracking, and collaboration tools that keep your content AI-ready.